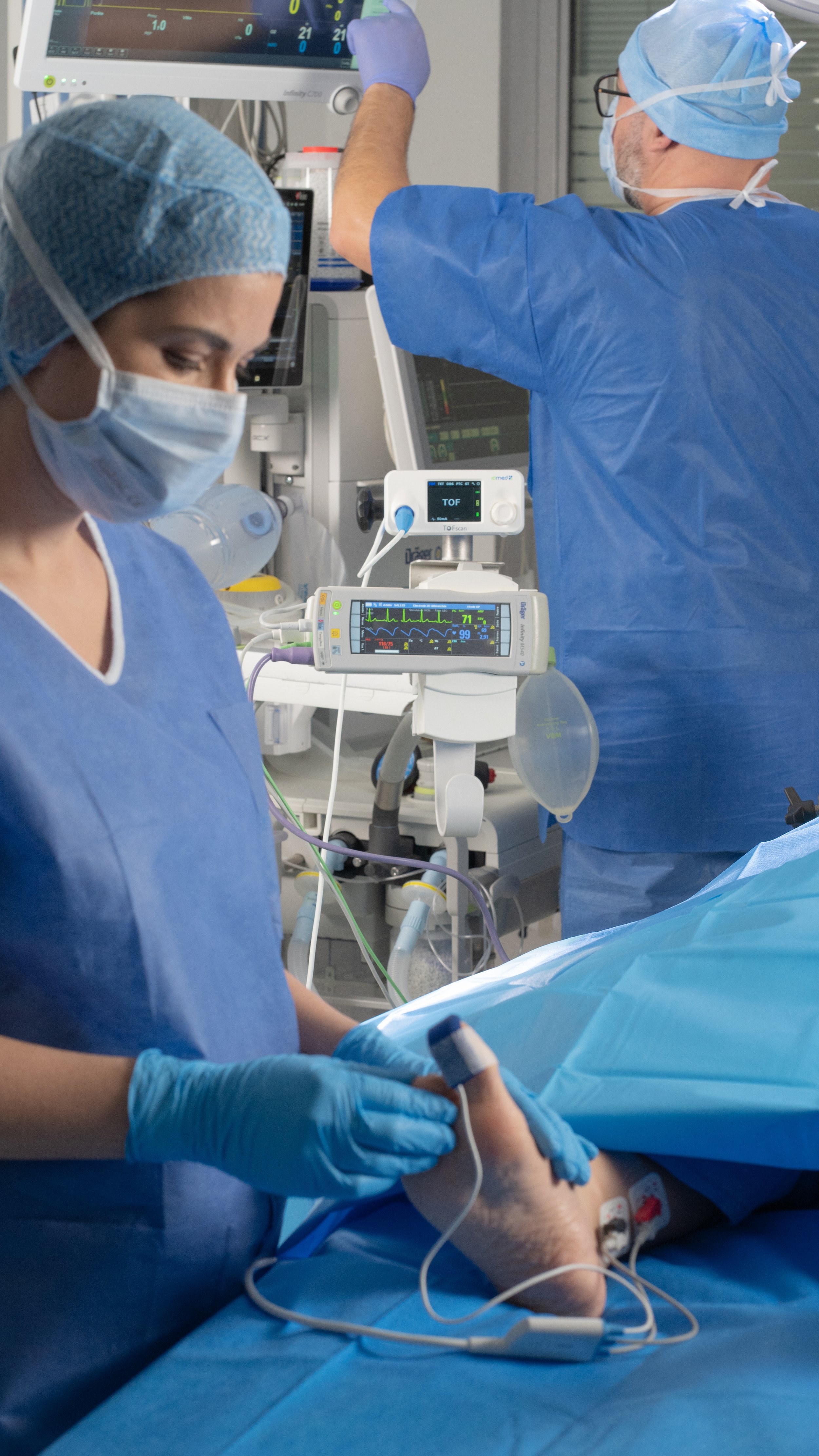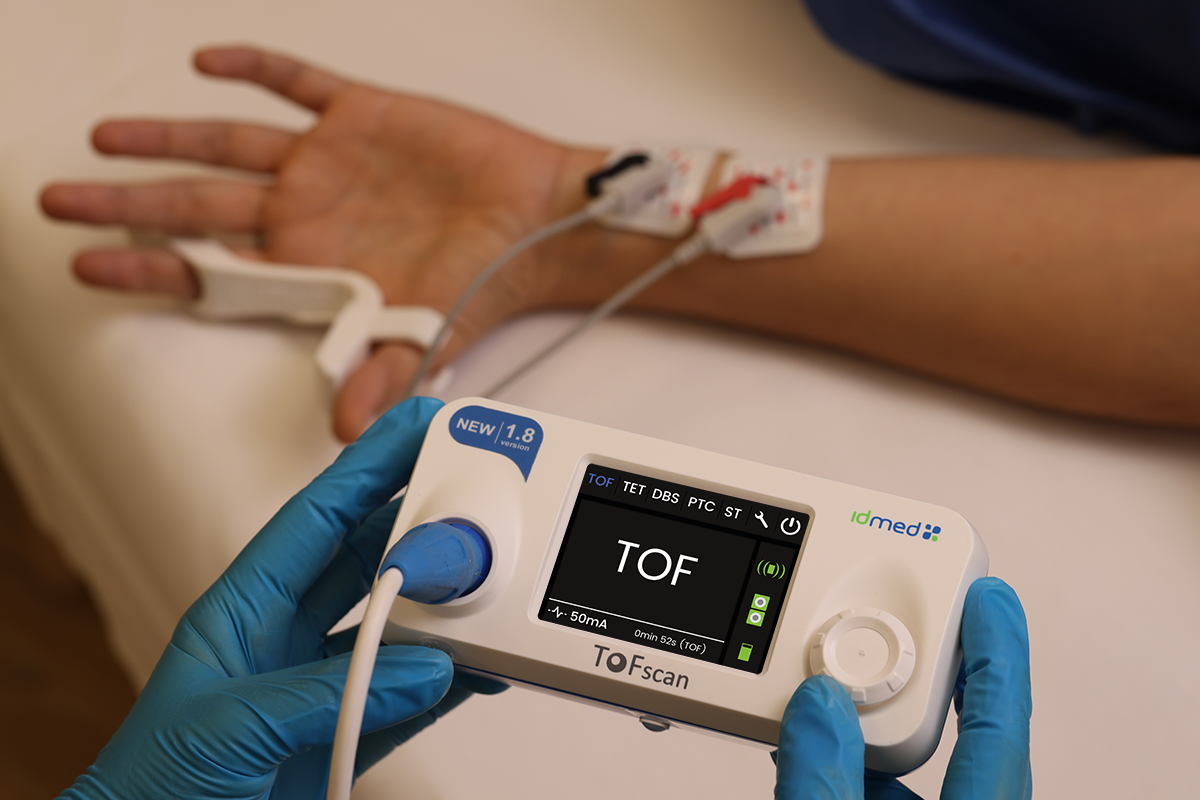
NMT MONITORING
Thanks to reusable sensors incorporating 3D-AMG technology, the ToFscan offers accurate, reliable assessment of patients' level of neuromuscular blockade, in line with ASA recommendations.
Adapted to all clinical environments, it ensures continuous monitoring and simplifies your daily practice.
Avoid residual paralysis
Residual neuromuscular block can significantly extend recovery, increasing the risk of serious clinical complications that can lead to increased hospital costs.
Quantitative TOF monitoring is currently the only method to exclude accurately and consistently RNMB.
Our solution to prevent residual paralysis
Enjoy unique clinical benefits of the ToFscan, an easy-to-use 3D-AMG TOF monitor and used worldwide in thousands of operating theaters and intensive care units for almost 10 years.
Precise and objective measures
Three-dimensional accelerometer (3D-AMG)
ATP automatic mode (TOF/PTC)
No calibration required
ToFscan, the TOF monitor for every patient
The most comprehensive range of dedicated sensors
The ToFscan has a range of sensors that answers to all the different medical practices in terms of Neuromuscular monitoring and recovery.
All ToFscan sensors use three-dimensional accelerometry technology. The 3D-AMG technology ensures reliable and accurate measurements and eliminates the need for any calibration process.
3D-AMG, is not AMG
The new 3D-AMG and its splint overcome weaknesses of widely accepted gold standard AMG.
ToFscan can be used on patients whether having received NMBAs, or not.
The ideal NMT monitor for a daily practice
RAPID SETUP.
No calibration is required.
COST-EFFICIENT.
Reusable sensors available and no proprietary consumables are required.
EASY-TO-USE.
Continuous and safe monitoring with the « auto pilot » ATP mode.
RELIABLE.
Reinforced immunity against electrosurgical unit interferences.
VERSATILE.
3D-AMG foot sensor available when hands are tucked at patient’s sides.
FOR EVERY PATIENT.
Reusable or single-use 3D-AMG sensors available for different stimulation sites.
Excellent in the ICU
The ToFscan NMT Monitor fits perfectly in the ICU
Individualised monitoring of your patients
Optimisation of NMBDs dosage
Diagnosis of prolonged neuromuscular blockade
Monitoring of spontaneous recovery
For a smooth practice in intensive care
For safe endotracheal intubation
Ensure ventilator-patient synchrony
To maintain the desired level of block
Integrates into the ICU workflow
No calibration required
Rechargeable battery
Electronic data transfer
Quick decontamination
ToFscan – the TOF Monitor for every patient
Technical Data
Stimulation
TOF (Train Of Four)
Automatic TOF
ATP (Automatic TOF-PTC)
PTC
DBS (3.3, 3.2)
Single Twitch (0,1 ; 1 Hz)
Tetanus 50 Hz
Measurements (3D Accelerometry
TOF mode : T4/T1
TOF mode : T4/Tref
TOF mode : count
PTC mode : count
DBS mode : count
Ergonomics
Three-dimensional accelerometer sensor
Adjustable stimulation current (20-60 mA)
Automatic switch-off
Battery and mains operated
Audio message (can be switched off)
Fixing clamp for bracket
No calibration required
Standards and safety
EN 60601-1 (Medical Electrical Equipment)
EN 60601-1-2 (EMC)
2A CE Class (CE 0459)
FDA Approved 510k
Recommendations Worldwide
Many societies and their national association of anesthetists around the world recommend NMT quantitative monitoring in their national guidelines for the management of neuromuscular blockade.
REFERENCES
*Depreciated over 5-year usable life span. Include sensors, disposables, and 30 monitors. The same calculation method has been used for EMG and 3D-AMG.
Comparison of the Tetragraph (EMG) and ToFscan (3D-AMG) for monitoring recovery from neuromuscular blockade in the Post Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU). DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2021.110234
Comparison of the TOFscan (3D-AMG) and the TOF-Watch SX (AMG) during Recovery of Neuromuscular Function. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000002400
Lori-Ann Edwards, et al. Perioperative Care and Operating Room Management, ISSN: 2405-6030, Vol: 24, Page: 100184. 2021
Multicenter Study of the Incidence and Severity of Residual Neuromuscular Blockade DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000757
Neuromuscular monitoring and neuromuscular blocking agent shortages when treating critically ill COVID-19 patients: a multicentre retrospective analysis DOI: 10.1016/j.bja.2021.04.028.
Technologies to Optimize the Care of Severe COVID-19 Patients for Health Care Providers Challenged by Limited Resources DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000004985
How to reduce cisatracurium consumption in ARDS patients: the TOF-ARDS study DOI: 10.1186/s13613-017-0305-2
Neuromuscular blockade management in patients with COVID-19 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4097/kja.21106
6A comparison of two depths of prolonged neuromuscular blockade induced by cisatracurium in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients DOI: 10.1007/s00134-002-1508-yCurrent Use of Neuromuscular Blocking Agents in Intensive Care Units DOI: 10.5152/TJAR.2019.33269
8Neuromuscular Blockade in the 21st Century Management of the Critically Ill Patient DOI: 10.1016/j.chest.2016.10.040Considerations in Neuromuscular Blockade in the ICU: A Case Report and Review of the Literature DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8780979